What Animal Is At The Top Of The Food Chain On Land
Life on the Nutrient Concatenation
Have you lot always wondered why we tin't seem to feed the world's hungry? Information technology's a complex effect, but it might surprise you to learn that it'due south not because there isn't enough nutrient; current agricultural capacity, based on electric current technology, exists to feed every bit many every bit ten billion people. The Earth's population is "only" about vii billion. The big question really is: If we want to feed anybody, what would everyone need to swallow? To respond that question, download this excel spreadsheet and attempt plugging in some numbers.
Example: One acre of a grain crop could be used to feed cattle, and then the cattle could be used to feed people. If fifty% of the energy is lost to the cattle, you could feed twice as many people if you fed them the grain directly. Another way of looking at it is that it would only take a half acre of country to feed the people grain, but a whole acre if you feed the grain to the cattle and the cattle to the people. A common practice to abound cattle faster is to feed them footing up fauna protein. This ways that when we eat the meat from the cow, we're at the tertiary level or higher. The loss of energy between trophic levels may likewise be even college. Recent studies suggest that only ~10% of energy is converted to biomass from one trophic level to the next!
The Food Concatenation: The respond has to do with trophic levels. As y'all probably know, the organisms at the base of the nutrient chain are photosynthetic; plants on land and phytoplankton (algae) in the oceans. These organisms are called the producers, and they become their energy directly from sunlight and inorganic nutrients. The organisms that eat the producers are the primary consumers. They tend to be small in size and in that location are many of them. The primary consumers are herbivores (vegetarians). The organisms that eat the primary consumers are meat eaters (carnivores) and are called the secondary consumers. The secondary consumers tend to be larger and fewer in number. This continues on, all the mode up to the top of the food concatenation. Well-nigh fifty% of the energy (possibly as much as 90%) in food is lost at each trophic level when an organism is eaten, then it is less efficient to be a higher order consumer than a main consumer. Therefore, the energy transfer from one trophic level to the next, up the food chain, is similar a pyramid; wider at the base and narrower at the top. Because of this inefficiency, in that location is only enough food for a few top level consumers, but there is lots of food for herbivores lower down on the nutrient chain. There are fewer consumers than producers.
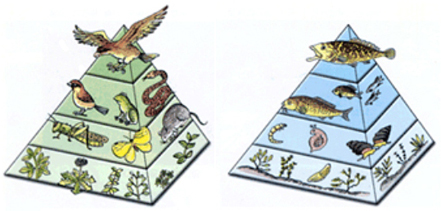
State and aquatic free energy pyramids
| Trophic Level | Desert Biome | Grassland Biome | Pond Biome | Ocean Biome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer (Photosynthetic) | Cactus | Grass | Algae | Phytoplankton |
| Primary Consumer (Herbivore) | Butterfly | Grasshopper | Insect Larva | Zooplankton |
| Secondary Consumer (Carnivore) | Lizard | Mouse | Minnow | Fish |
| Third Consumer (Carnivore) | Snake | Serpent | Frog | Seal |
| Quaternary Consumer (Carnivore) | Roadrunner | Hawk | Raccoon | Shark |
Nutrient Spider web: At each trophic level, in that location may be many more species than indicated in the tabular array above. Food webs tin can be very complex. Food availability may vary seasonally or past fourth dimension of day. An organism like a mouse might play 2 roles, eating insects on occasion (making it a secondary consumer), only also dining directly on plants (making it a chief consumer). A food spider web of who eats who in the southwest American desert biome might look something like this:
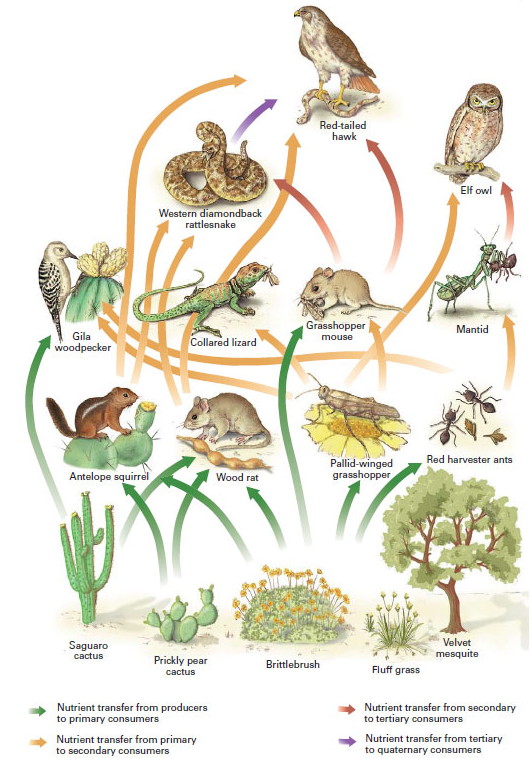
image source: http://iqa.evergreenps.org/science/biology/ecosystem_files/food-web.jpg
Keystone Species: In some food webs, there is 1 critical "keystone species" upon which the entire system depends. In the same way that an arch collapses when the keystone is removed, an entire food chain can plummet if in that location is a pass up in a keystone species. Often, the keystone species is a predator that keeps the herbivores in check, and prevents them from overconsuming the plants, leading to a massive die off. When nosotros remove top predators like grizzly bears, orca whales, or wolves, for case, in that location is evidence that it affects not just the prey species, but even the physical environment.
Apex Predators: These species are at the top of the food chain and the healthy adults have no natural predators. The immature and old may in some cases be preyed upon, just they typically succumb to disease, hunger, the effects of crumbling, or some combination of them. The too suffer from competition with humans, who often eliminate the top predators in order to have exclusive access to the prey species, or through habitat devastation, which is an indirect form of competition.
Decomposers: When organisms dice, they are sometimes eaten by scavengers but the remaining tissues are broken downward by fungi and leaner. In this way, the nutrients that were role of the body are returned to the bottom of the trophic pyramid.
Bioaccumulation: In improver to being less energy efficient, eating higher up the food chain has its risks. Pesticides and heavy metals like mercury, arsenic, and lead tend to be consumed in small quantities past the primary consumers. These toxins become stored in the fats of the beast. When this brute is eaten past a secondary consumer, these toxins become more than concentrated considering secondary consumers eat lots of master consumers, and oft live longer besides. Swordfish and tuna are most the top of the aquatic food concatenation and, when we eat them, we are consuming all of the toxins that they have accumulated over a lifetime. For this reason, meaning women are advised confronting eating these foods.
Solve the following issues mathematically.
1. Given: 10 billion people can be fed a basic vegetarian diet that is nutritionally complete. How many people could we feed at the American standard-a tertiary level of consumption (3rd order consumers?). 50% of the free energy is lost by each higher level.
2. If there are 250 million people in the United States most of them eating at the Tertiary (3rd) level of consumption, how many people could we feed at the Primary level?
iii. Some animals like sharks are fifth order consumers! Sharks consume tuna that eat mackerel that eat herring that consume copepods that eat diatoms. If nosotros were to brand the reasonable assumption that each of these animals eats 2 of its prey each twenty-four hour period, how many organisms died to feed the shark in one day?
Source: https://www2.nau.edu/lrm22/lessons/food_chain/food_chain.html
Posted by: cornettinglacrievor.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Animal Is At The Top Of The Food Chain On Land"
Post a Comment